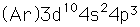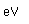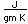Arsenic
Ordinary gray arsenic is a semi-metallic substance, steel-gray in color with density 5.73. There is also an unstable yellow crystalline form containing As4 molecules, similar to the structure of phosphorus.
Sulfides
In nature arsenic is found in several ores. Orpiment, As2S3, is a yellow substance while realgar, AsS, is a red substance. It is also found in the oxide arsenolite, As4O6, and in arsenopyrite, FeAsS. A sulfide with copper is called enargite. Dufrenoysite and gratonite are sulfides of arsenic with lead. A sulfide formed with lead and antimony is called jordanite. Arsenic forms a sulfide mineral with nickel called gersdorffite. Tennantite is a sulfide which contains arsenic, copper, iron and antimony. Arsenic joins with iron and cobalt in the sulfide glaucodot. Arsenic with silver forms the sulfide proustite. In the sulfide mineral hutchinsonite, (Tl, Pb)2As5S9, arsenic joins with thallium and lead.
Arsenic forms a compound with platinum, PtAs2 which appears in the mineral sperrylite. Iron with arsenic forms the mineral loellingite, FeAs2. Cobalt and arsenic form the minerals safflorite, CoAs2 and cobaltite, CoAsS.
Cobalt and nickel form the minerals skutterudite, CoAs2-3 and nickel-skutterudite, NiAs2-3 Stibarsen, SbAs, is a silvery mineral with a metallic luster.
Arsenates with copper and zinc such as bayldonite, adamite and olivenite have a deep green color. Another green mineral is the copper arsenate tyrolite. See also the zinc arsenate paradamite. The zinc arsenate legrandite has a dramatic orange color. Another zinc arsenate is kottigite. Ludlockite is an arsenate with iron and lead and has a coppery red color. Mimetite, an arsenate of lead with chlorine, forms yellow crystals. Scorodite is an arsenate of iron (dark blue color) and reinerite is an arsenate of zinc. Bayldonite is an arsenate that contains copper, lead and zinc. Roselite is an arsenate that contains cobalt, magnesium and calcium and forms red crystals. Erythrite is an arsenate of cobalt and also shows a red or rose color. Duftite is an arsenate mineral of lead and copper. Liroconite is an arsenate mineral of aluminum and copper with a blue color. Another copper-containing mineral is chalcophyllite.
Arsenic appears with manganese and magnesium in the silicate Ardennite. It appears with titanium, manganese and iron in the mineral cafarsite. Arsenic with magnesium, manganese and zinc forms the silicate Mcgovernite.
Arsenic is used with lead (0.5% As) in making lead shot. It makes the metal harder than the pure lead and improves the properties of the molten material. The shot is formed by pouring the molten material through a screen at the top of a tower and allowing it to solidify into spherical balls before reaching water in a collecting vessel at the bottom of the tower.
Arsine, AsH3, is a very poisonous gas with a garlic-like odor. Arsenic metal is very toxic, as are many of its compounds. Cupric hydrogen arsenate and a cupric arsenic-acetate (called Paris green) are used as insecticides. Sodium arsenate, Na3AsO4,is used as a weed killer, and calcium arsenate is used as an insecticide. The toxicity of arsenic compounds is sometimes used to advantage in medicine by devising chemotherapy where arsenic compounds at lower than poisonous doses to man are used to attack invading microorganisms.

|
Arsenic is one of the few elements which can be found in nature in pure form. This sample of arsenic is displayed in the Smithsonian Museum of Natural History. The left sample is about 18x18 cm and is from Andreasberg, Niedersachsen, Germany.
|
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 16 |