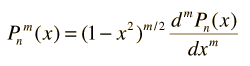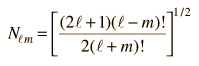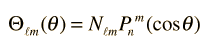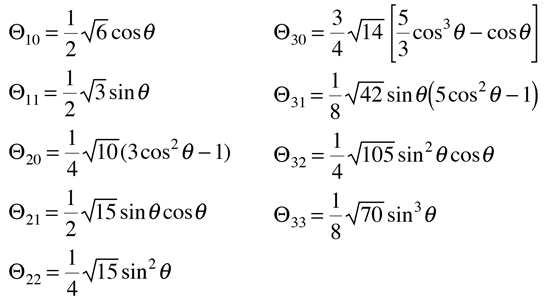Legendre Polynomials
One of the varieties of special functions which are encountered in the solution of physical problems is the class of functions called Legendre polynomials. They are solutions to a very important differential equation, the Legendre equation:
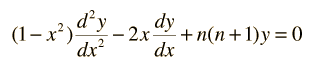
The polynomials may be denoted by Pn(x) , called the Legendre polynomial of order n. The polynomials are either even or odd functions of x for even or odd orders n. The first few polynomials are shown below.
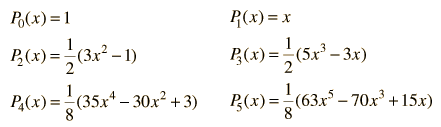
The general form of a Legendre polynomial of order n is given by the sum:
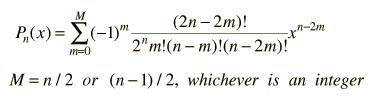
From the Legendre polynomials can be generated another important class of functions for physical problems, the associated Legendre functions.
The equation takes its name from Adrien Marie Legendre (1752-1833), a French mathematician who became a professor in Paris in 1775. He made important contributions to special functions, elliptic integrals, number theory, and the calculus of variations. (Kreyszig).
Reference
Kreyszig
Sec 4.3
| HyperPhysics*****HyperMath*****Calculus | R Nave |