System Matrix for a Thick Lens
This is an examination of the system matrix for a thick lens in the form used by Meyer-Arendt. An alternative form of the system matrix is used by Hecht.
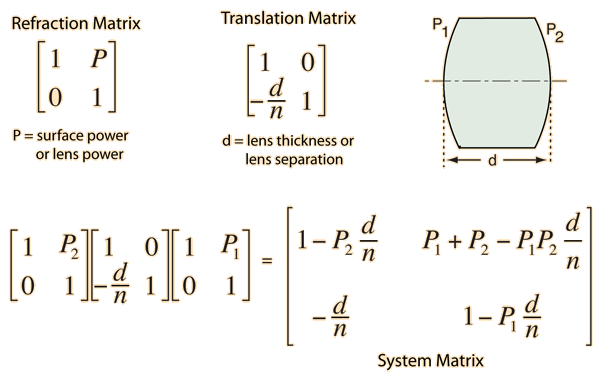
The example is for a lens with index of refraction n surrounded by air (n=1). It involves the surface powers of the lens and the thickness d between the vertexes. It also involves the principal planes H1 and H2. As with most ordinary geometrical optics, it is applicable only for small angles (paraxial rays). The development also follows the cartesian sign convention.
| Image location for thick lens from system matrix |
| Image location for pair of thin lenses from system matrix |
Lens concepts
Thick lens concepts
References
Meyer-Arendt
Ch. 1.4
Hecht
| HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision | R Nave |