ΛCDM
Lambda Cold Dark Matter Concordance Model
In recent years there has been an intensive study of the expanding universe and Hubble's Law. Many experiments and lines of modeling have contributed to the evaluation of the universe's expansion. After the earlier COBE and WMAP satellite data, the Planck satellite collected data for 4.5 years and as of 2020 provides the most accurate evaluation of the CMB radiation. The graphical history of Hubble's Law evaluation shown below is from the NASA publication on the Hubble Constant, H0.
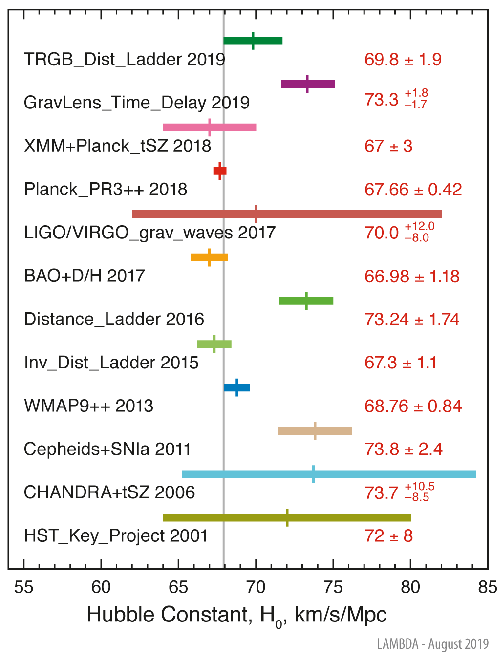
Image Credit NASA | This plot compares values for H0 derived from a variety of methods. It includes 2016 and 2019 values from the distance ladder which builds from successive methods. It also includes a value from the observation of gravity waves, which is independent of that distance ladder. |
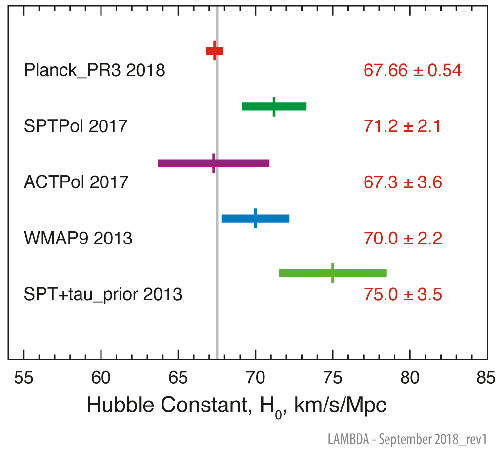
Image Credit NASA | This plot compares values for H0 derived from the CMB only. |
After the extensive data from the Planck satellite was received, the 2015 reports from the Planck Collaboration presented descriptive parameters for the universe in the ΛCDM concordance model:
| Parameter | Measured Value |
| Normal Matter Density, Ωb | 0.0486 +/- 0.0003 |
| Dark Matter Density, Ωc | 0.2589 +/- 0.0022 |
| Space-Energy Density, ΩΛ | 0.6911 +/- 0.0062 |
| Curvature Ωk (0 => flat) | 0.0008 +/- 0.0040 |
| Hubble constant, H0 | 67.74 +/- 0.46 km/s/megaparsec |
| Age of the universe, Tuniv | 13.799 +/- 0.0040 billion years |
| Spectral Index, ns | 0.9667 +/- 0.0040 |
|
Index
NASA, Hubble Constant |

