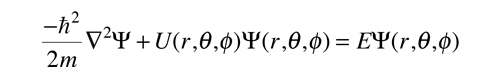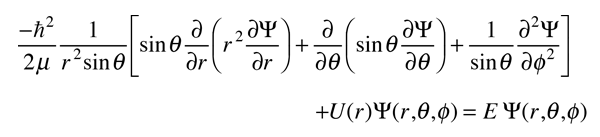3-D Schrodinger Equation
In three dimensions, the time-independent Schrodinger equation takes the form
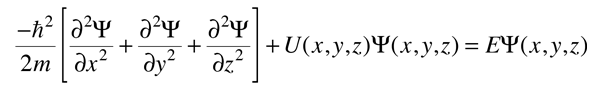
for cartesian coordinates. This can be written in a more compact form by making use of the Laplacian operator
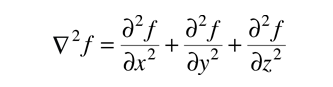
The Schrodinger equation can then be written:
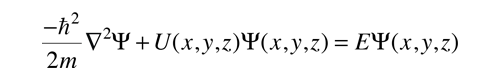
For systems with a spherically symmetric potential, like the hydrogen atom, it is advantageous to use spherical coordinates.
Schrodinger equation concepts