Eigenvalues and Eigenfunctions
The wavefunction for a given physical system contains the measurable information about the system. To obtain specific values for physical parameters, for example energy, you operate on the wavefunction with the quantum mechanical operator associated with that parameter. The operator associated with energy is the Hamiltonian, and the operation on the wavefunction is the Schrodinger equation. Solutions exist for the time independent Schrodinger equation only for certain values of energy, and these values are called "eigenvalues*" of energy.
Corresponding to each eigenvalue is an "eigenfunction*". The solution to the Schrodinger equation for a given energy 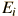 involves also finding the specific function
involves also finding the specific function 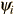 which describes that energy state. The solution of the time independent Schrodinger equation takes the form
which describes that energy state. The solution of the time independent Schrodinger equation takes the form
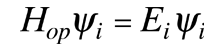
The eigenvalue concept is not limited to energy. When applied to a general operator Q, it can take the form
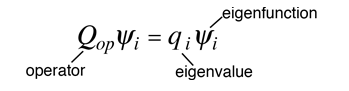
if the function ψi is an eigenfunction for that operator. The eigenvalues qi may be discrete, and in such cases we can say that the physical variable is "quantized" and that the index i plays the role of a "quantum number" which characterizes that state.
| Energy eigenvalues |
*"Eigenvalue" comes from the German "Eigenwert" which means proper or characteristic value. "Eigenfunction" is from "Eigenfunktion" meaning "proper or characteristic function".
Schrodinger equation concepts
Postulates of quantum mechanics
| HyperPhysics***** Quantum Physics | R Nave |