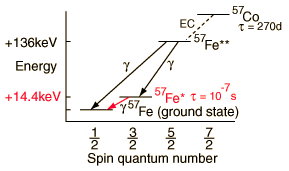
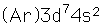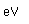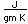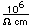Cobalt
Cobalt is a silvery-white metal, with a slight reddish tinge. It occurs in the minerals smaltite and safflorite with the composition CoAs2. Cobalt also forms an arsenide with the content CoAs2-3 which is called skutterudite. The sulfide mineral cobaltite, CoAsS, also occurs. Cobalt is usually found in association with nickel. Cobalt forms the sulfide mineral linnaeite, Co3S4. Copper, cobalt and nickel join in the sulfide carrollite, Cu(Co,Ni)2S4. Cobalt joins with iron and arsenic in the sulfide glaucodot, (Co,Fe)AsS. Cobalt and nickel form the sulfide siegenite, CoNi2S4. Roselite is an arsenate that contains cobalt, magnesium and calcium and forms red crystals. Erythrite is an arsenate of cobalt and also shows a red or rose color.
Cobalt is used to produce the strongly ferromagnetic alloy alnico which is used to make strong permanent magnets. Alnico alloys iron, nickel, cobalt and aluminum.
Cobalt chloride (CoCl2.6H2O) forms red crystals which turn blue when dehydrated. Cobalt oxide, CoO, is a black powder, but it gives a blue color to glass when dissolved in it (cobalt glass).
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 27 |