Critical Damping
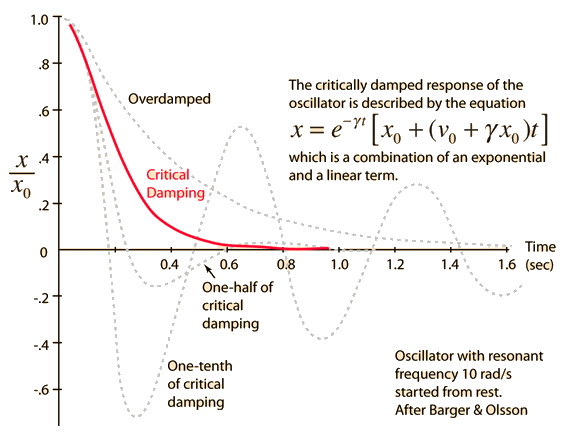
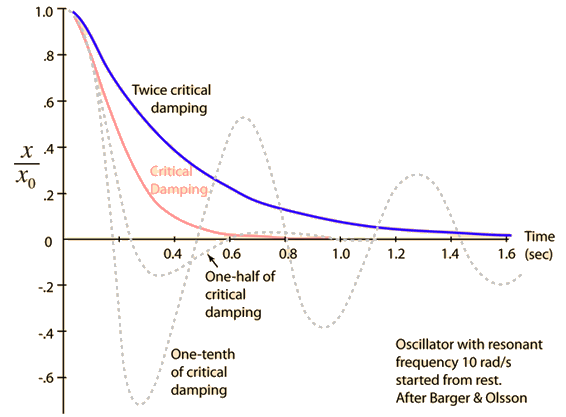
Critical damping provides the quickest approach to zero amplitude for a damped oscillator. With less damping (underdamping) it reaches the zero position more quickly, but oscillates around it. With more damping (overdamping), the approach to zero is slower. Critical damping occurs when the damping coefficient is equal to the undamped resonant frequency of the oscillator.
| Damped Oscillator | Underdamped oscillator | Overdamped oscillator |
Periodic motion concepts
Reference
Barger & Olsson
| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics | R Nave |