Mass and Weight
The mass of an object is a fundamental property of the object; a numerical measure of its inertia; a fundamental measure of the amount of matter in the object. Definitions of mass often seem circular because it is such a fundamental quantity that it is hard to define in terms of something else. All mechanical quantities can be defined in terms of mass, length, and time. The usual symbol for mass is m and its SI unit is the kilogram. While the mass is normally considered to be an unchanging property of an object, at speeds approaching the speed of light one must consider the increase in the relativistic mass.
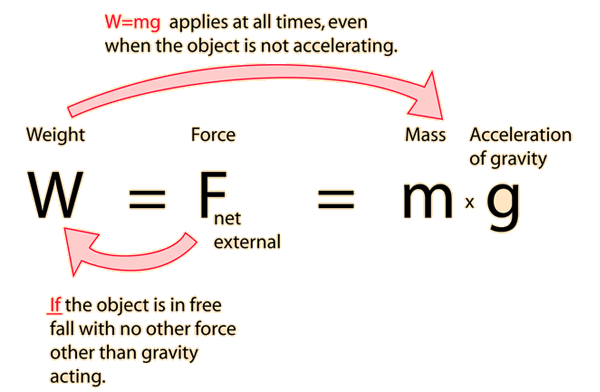
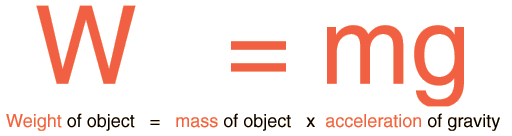
The weight of an object is the force of gravity on the object and may be defined as the mass times the acceleration of gravity, w = mg. Since the weight is a force, its SI unit is the newton. Density is mass/volume.

| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics | R Nave |