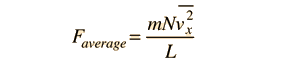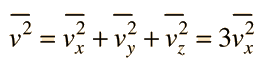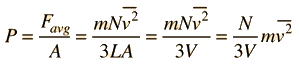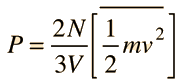Newton's Laws and Collisions
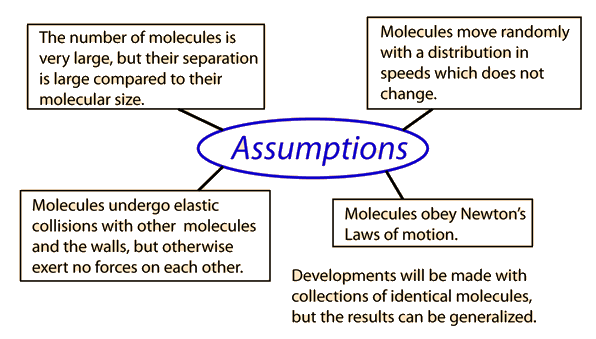
Applying Newton's Laws to an ideal gas under the assumptions of
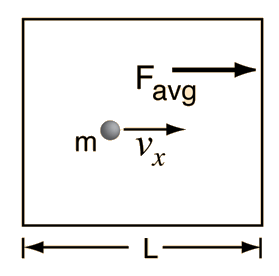
kinetic theory allows the determination of the average force on container walls. This treatment assumes that the collisions with the walls are perfectly elastic.
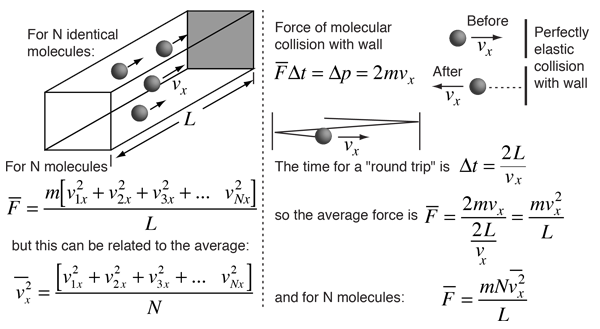
In this development, an overbar indicates an average quantity. In the expression for the average force from N molecules, it is important to note that it is the average of the square of the velocity which is used, and that this is distinctly different from the square of the average velocity.
|
Index
Kinetic theory concepts |