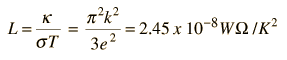Thermal Conductivity
| Material | Thermal conductivity
(cal/sec)/(cm2 C/cm) | Thermal conductivity
(W/m K)* |
| Diamond | ... | 1000 |
| Silver | 1.01 | 406.0 |
| Copper | 0.99 | 385.0 |
| Gold | ... | 314 |
| Brass | ... | 109.0 |
| Aluminum | 0.50 | 205.0 |
| Iron | 0.163 | 79.5 |
| Steel | ... | 50.2 |
| Lead | 0.083 | 34.7 |
| Mercury | ... | 8.3 |
| Ice | 0.005 | 1.6 |
| Glass,ordinary | 0.0025 | 0.8 |
| Concrete | 0.002 | 0.8 |
| Water at 20° C | 0.0014 | 0.6 |
| Asbestos | 0.0004 | 0.08 |
| Snow (dry) | 0.00026 | ... |
| Fiberglass | 0.00015 | 0.04 |
| Brick,insulating | ... | 0.15 |
| Brick, red | ... | 0.6 |
| Cork board | 0.00011 | 0.04 |
| Wool felt | 0.0001 | 0.04 |
| Rock wool | ... | 0.04 |
| Polystyrene (styrofoam) | ... | 0.033 |
| Polyurethane | ... | 0.02 |
| Wood | 0.0001 | 0.12-0.04 |
| Air at 0° C | 0.000057 | 0.024 |
| Helium (20°C) | ... | 0.138 |
| Hydrogen(20°C) | ... | 0.172 |
| Nitrogen(20°C) | ... | 0.0234 |
| Oxygen(20°C) | ... | 0.0238 |
| Silica aerogel | ... | 0.003 |
*Most from Young, Hugh D., University Physics, 7th Ed. Table 15-5. Values for diamond and silica aerogel from CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics.
Note that 1 (cal/sec)/(cm2 C/cm) = 419 W/m K. With this in mind, the two columns above are not always consistent. All values are from published tables, but can't be taken as authoritative.
The value of 0.02 W/mK for polyurethane can be taken as a nominal figure which establishes polyurethane foam as one of the best insulators. NIST published a numerical approximation routine for calculating the thermal conductivity of polyurethane at http://cryogenics.nist.gov/NewFiles/Polyurethane.html . Their calculation for freon filled polyurethane of density 1.99 lb/ft3 at 20°C gives a thermal conductivity of 0.022 W/mK. The calculation for CO2 filled polyurethane of density 2.00 lb/ft3 gives 0.035 W/mK .
|
Index
Tables
Reference
Young
Ch 15. |