Critical Magnetic Field and Critical Current
It is the nature of superconductors to exclude magnetic fields (Meissner effect) so long as the applied field does not exceed their critical magnetic field. This critical magnetic field is tabulated for 0K and decreases from that magnitude with increasing temperature, reaching zero at the critical temperature for superconductivity. If the critical magnetic field is exceeded, the material makes a transition out of superconductivity to normal conductivity. The critical magnetic field at any temperature below the critical temperature is given by the relationship
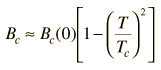
| Illustrate mixed state | Examples |
| Table of critical fields and temperatures |
Superconductivity concepts
Reference Rohlf,Ch 15
| HyperPhysics***** Condensed Matter | R Nave |