The Genetic Code
Active graphic
| Remove superimposed code |
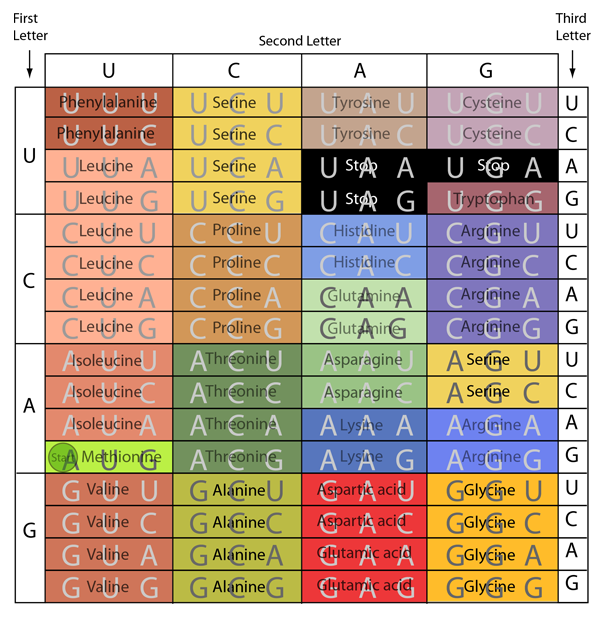
The genetic code by which DNA stores the genetic information consists of "codons" of three nucleotides. The functional segments of DNA which code for the transfer of genetic information are called genes. With four possible bases, the three nucleotides can give 43 = 64 different possibilities, and these combinations are used to specify the 20 different amino acids used by living organisms.
The ribonucleic acid (RNA) that is directly involved in the transcription of the pattern of bases from the DNA to provide a blueprint for the construction of proteins is called messenger RNA or typically mRNA. The pattern for protein synthesis is then read and translated into the language of amino acids for protein construction with the help of transfer RNA or tRNA.Biochemical concepts
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Karp
Ch 11
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry *****Biology | R Nave |