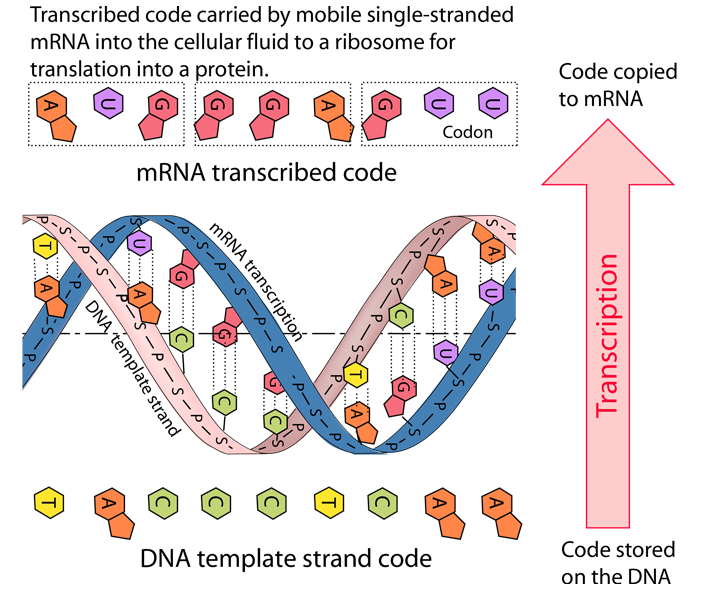
DNA to RNA Transcription
The DNA contains the master plan for the creation of the proteins and other molecules and systems of the cell, but the carrying out of the plan involves transfer of the relevant information to RNA in a process called transcription. The RNA to which the information is transcribed is messenger RNA (mRNA).
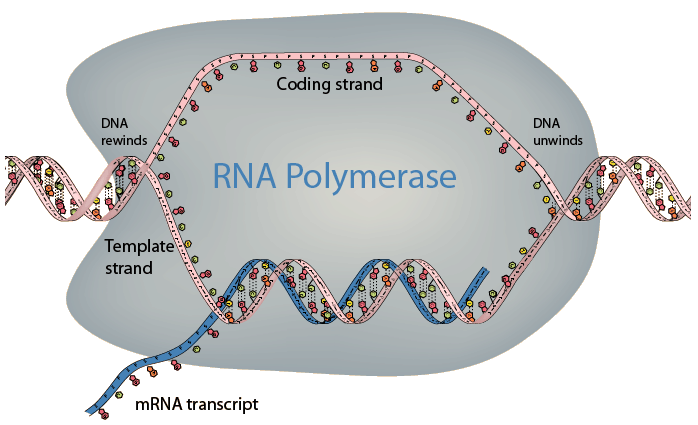
The process associated with RNA polymerase is to unwind the DNA and build a strand of mRNA by placing on the growing mRNA molecule the base complementary to that on the template strand of the DNA. In the mRNA, Uracil is substituted for thymine as the base complementary to adenine. Since the other strand of the DNA has bases complementary to the template strand, the mRNA has the same sequence of bases at the upper strand of DNA shown above (with U substituted for T) , which is called the coding strand. According to Karp, the RNA polymerase is capable of adding 20 to 50 nucleotides per second to the growing mRNA chain. Electron microscope images suggest that there can be over a hundred RNA polymerases operating simultaneously.
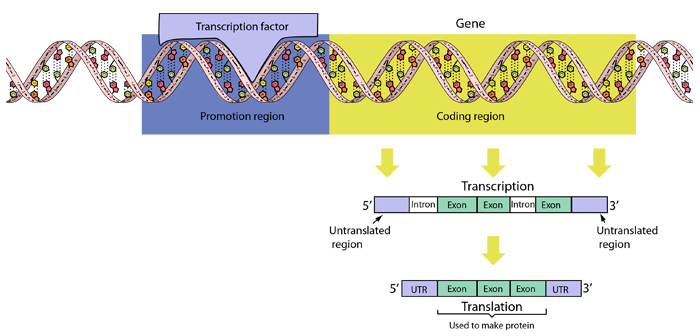
A coding region of the DNA for a specific protein (a gene) contains the pattern for the creation of the protein. The coding region is preceded by a promotion region, and a transcription factor binds to that promotion region of the DNA. It recruits the necessary RNA polymerase to activate the copying of the pattern of the coding region over to RNA. The segment of DNA transcribed to the RNA contains some material that is not translated on both the beginning (5') and end (3') of the segment. It also typically has segments called introns that are not translated as well as segments called exons that are actually part of the pattern for the protein.
| Transcription of a short segment | Translation |
Biochemical concepts
Chemistry concepts
References
Karp
Sec 11.2
| HyperPhysics*****Biology | R Nave |