Alcohols
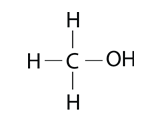
Alcohols are organic compounds containing a hydroxyl group, -OH, substituted for a hydrogen atom. The names of alcohols start with the name of the alkane but end with the suffix -ol, like the simplest alcohol, methanol.
 |
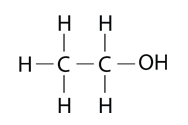
Ethanol is the alcohol in alcoholic beverages and it is also widely used as a solvent.
 |
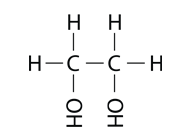
Alcohols can have more than one hydroxyl group. Ethylene glycol, used as antifreeze in automobiles, has two hydroxyl groups.
 |
| Retinol (Vitamin A) |
| Hydrocarbon derivatives |
Carbon compounds
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Shipman, Wilson, Todd
Sec 15.4
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry | R Nave |