Alkenes
| Aliphatic hydrocarbons with one double bond between carbons are called alkenes. They follow the naming convention of the alkanes except that the suffix -ene is used instead of -ane. For alkenes above propene the position of the double bond must be specified in the name. |
ethylene |  | 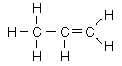 | propene |
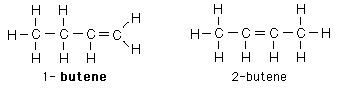
The double bond in alkenes can act to bond such molecules together in long chains and sheets. The formation of polymers is an important area of chemistry.
| Aliphatic Hydrocarbons |
Carbon compounds
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Shipman, Wilson, Todd
Sec 15.2
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry | R Nave |