Particle Interactions in the Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics seeks to describe the electromagnetic, weak, and strong interactions of particles. At present, there is no comparable quantum mechanical treatment of gravity , the fourth fundamental force. The Standard Model describes the particles which are the building blocks of the universe including quarks (which make up protons and neutrons) and leptons (which include electrons) as well as force carrying particles which influence the quarks and leptons.
 Active graphic, click at any point
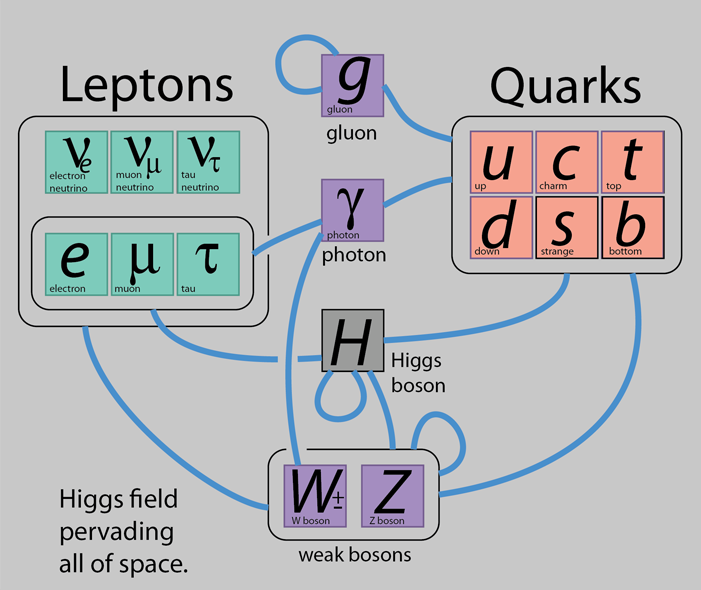
Active graphic, click at any pointThe diagram above includes the fundamental particles of the Standard Model and indicates the interactions between those particles with blue lines. The diagram is patterned after the treatment by Mustafa Ashry. The Higgs field is constant throughout space so the resulting mass contribution is the same at any point. The photon and gluons are bosons that do not interact with the Higgs field and are considered to be massless vector bosons. The particles that do interact are given masses that are proportional to the strength of that interaction. The W and Z particles are the exchange particles associated with the nuclear weak interaction. They interact strongly with the Higgs field and therefore have large masses and short ranges. The extremely small neutrino mass suggests a very weak if non-zero interaction with the Higgs field.
The gluons are the exchange particles for the strong force and interact with all the quarks.The looping interaction line is a reminder that gluons interact with other gluons in the process of building massive fermions like protons. Photons carry the electromagnetic force, indicated by connecting lines to the quarks, lepton particles, and the charged weak boson W. The Higgs boson represents the interaction which provides mass to all the massive particles, and the looping interaction indicates interaction with other Higgs bosons. The W and Z weak bosons are the exchange particle for the weak interaction and connect to all quarks and leptons and the Higgs boson. The looping line indicates interaction with each other.
| The Path to the Higgs |
| The Atlas and CMS Experimental Detection |
| The Higgs Field |
| Mass and its relationship to the Higgs Field |
Ashry, Mustafa, Higgs Field and the Origin of Mass.
Fundamental force concepts
Higgs Vimeo
Higgs Vimeo
Atlas bulletin on Higgs
Higgs boson Wiki
| HyperPhysics***** Quantum Physics | R Nave |