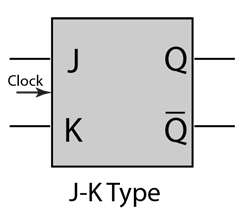
J-K Flip-Flop
|
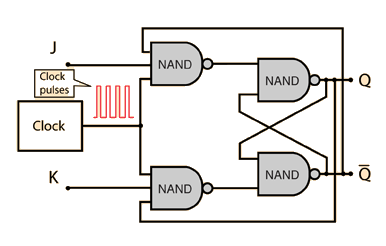
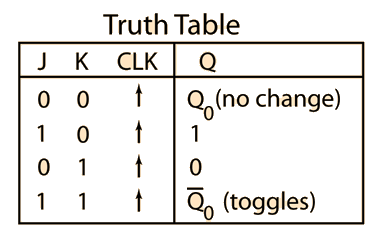
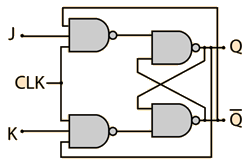
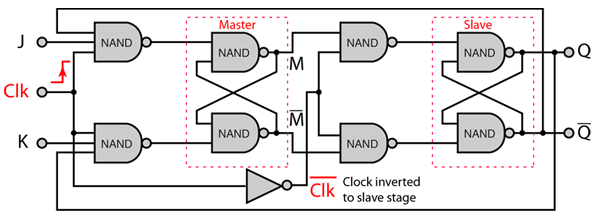
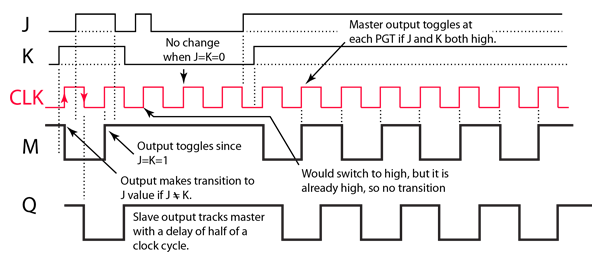
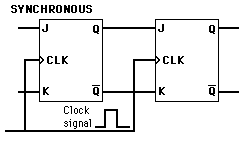
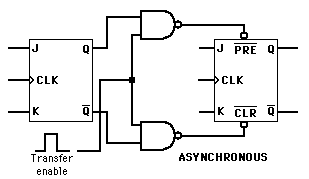
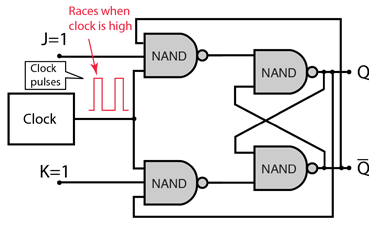
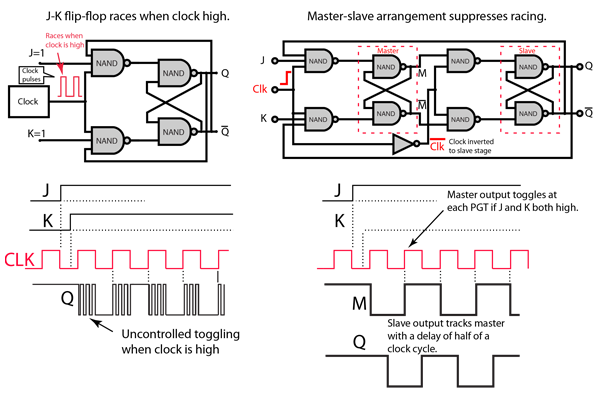
The J-K flip-flop is the most versatile of the basic flip-flops. It has the input- following character of the clocked D flip-flop but has two inputs,traditionally labeled J and K. If J and K are different then the output Q takes the value of J at the next clock edge. The inputs are labeled J and K in honor of the inventor of the device, Jack Kilby.
|
 |
If J and K are both low then no change occurs. If J and K are both high at the clock edge then the output will toggle from one state to the other. It can perform the functions of the set/reset flip-flop and has the advantage that there are no ambiguous states. It can also act as a T flip-flop to accomplish toggling action if J and K are tied together. This toggle application finds extensive use in binary counters.
| Flip-Flops |
Electronics concepts
Digital circuits
Sequential Operations
J-K Flip-Flop Applications
| HyperPhysics*****Electricity and magnetism | R Nave |