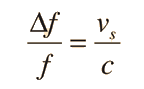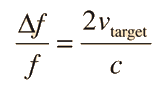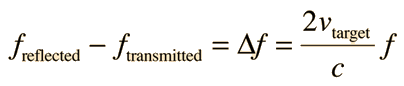Police RADAR
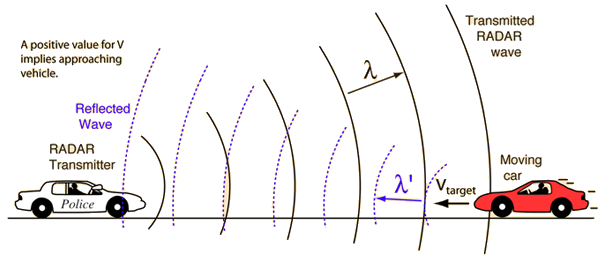
RADAR speed detectors bounce microwave radiation off of moving vehicles and detect the reflected waves. These waves are shifted in frequency by the Doppler effect, and the beat frequency between the directed and reflected waves provides a measure of the vehicle speed.
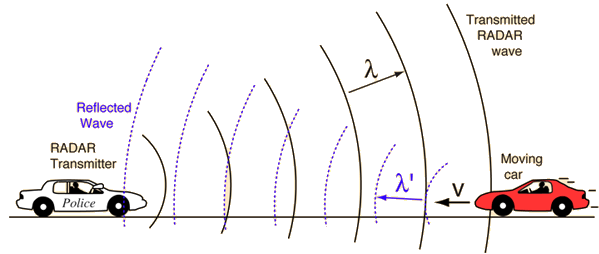
| Speed detection calculation |
Traveling wave concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Sound | R Nave |