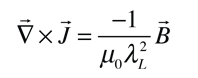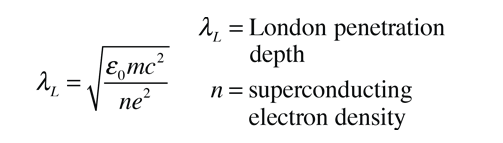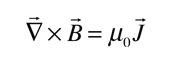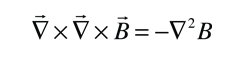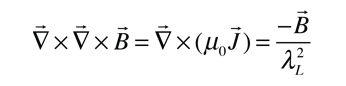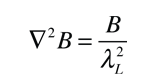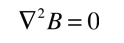Characteristic Lengths in Superconductors
Arising in the theoretical and experimental investigations of superconductivity are two characteristic lengths, the London penetration depth and the coherence length.
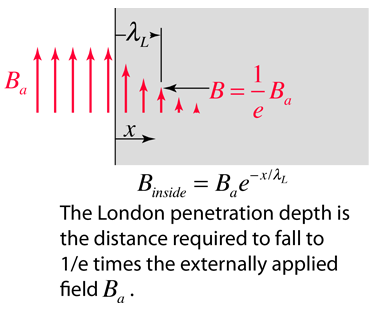
The London penetration depth refers to the exponentially decaying magnetic field at the interior surface of a superconductor. It is related to the density of superconducting electrons in the material. The fact of exclusion of magnetic fields from the interior of the superconductor is called the Meissner effect.
An independent characteristic length is called the coherence length. It is related to the Fermi velocity for the material and the energy gap associated with the condensation to the superconducting state. It has to do with the fact that the superconducting electron density cannot change quickly - there is a minimum length over which a given change can be made, lest it destroy the superconducting state. For example, a transition from the superconducting state to a normal state will have a transition layer of finite thickness which is related to the coherence length. Experimental studies of various superconductors have led to the following calculated values for these two types of characteristic lengths.
| Material | Coherence length
ξ0(nm) | London penetration depth
λL(nm) | Ratio
λL/ξ0 |
| Sn | 230 | 34 | 0.16 |
| Al | 1600 | 16 | 0.010 |
| Pb | 83 | 37 | 0.45 |
| Cd | 760 | 110 | 0.14 |
| Nb | 38 | 39 | 1.02 |
Data attributed to R. Meservey and B. B. Schwartz.
|