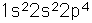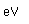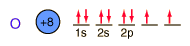Oxygen
Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth's crust, making up about 46.6% by weight of the crust. It constitutes 89% of water by weight, 23% of the air, and nearly 50% of common silicate minerals. It is also present in carbonate, sulfate and phosphate minerals as well as in oxide minerals. As a gas, it exists as a diatomic molecule O2.
Ordinary combustion is the process of combining oxygen with other substances. The energy required for bodily warmth and the physical and chemical process of living organisms is obtained from the combination of oxygen with organic material in food.
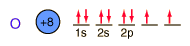
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 6 |