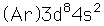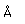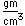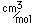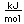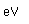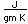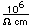Nickel
Nickel is a white metal, with a faint tinge of yellow. It is used widely in making alloys, including copper-nickel (75% copper, 25% nickel) which is used in coinage.
Nickel is used in the production of the strongly ferromagnetic alloy alnico which is used to make strong permanent magnets. Alnico alloys iron, nickel, cobalt and aluminum.
Stainless steel contains 12-18% chromium and usually about 8% nickel.
Iron objects can be plated with nickel for corrosion resistance.
The principal ores of nickel are nickelite (NiAs), millerite (NiS), and pentlandite ((Ni,Fe)S. Nickel forms a sulfide mineral with arsenic called gersdorffite. Nickel forms another arsenide called nickel-skutterudite, NiAs2-3. The sulfide formed with antimony is called ullmannite. Copper, cobalt and nickel join in the sulfide carrollite, Cu(Co,Ni)2S4. Cobalt and nickel form the sulfide siegenite, CoNi2S4. Nickel is often found in association with iron and sometimes forms the compound Ni3Fe, called awaruite in its mineral form. Nickel-iron meteorites are fairly common. A major source of nickel is the Sudbury Basin in Canada associated with the second largest meteoritic impact crater on the Earth.
Nickel is used in alloy with gold to make "white gold" for jewelry use.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 29 |