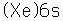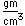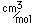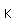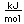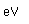Cesium
The compounds of cesium are similar to those of potassium. This presents a particular hazard when radioactive cesium-137 contaminates the soil, as it did near Chernobyl. Growing plants require large amounts of potassium, and concentrate it from the soil. Since cesium mimics potassium, the radioactive cesium is also taken up and reconcentrated. The result is that plants grown on contaminated soil may contain a much higher concentration of radioactive cesium than the soil in which they are grown.
The electron configuration of cesium consists of one lone 6s electron outside a perfectly symmetrical core of 54 other electrons characteristic of the noble element xenon. This fact has made it the foundation for mankind's best clock, the cesium atomic clock.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 26 |