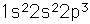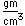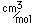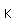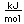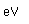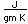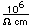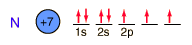Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas which is composed of diatomic molecules N2. It constitutes 78% of the air by volume. At 0°C and 1 atmosphere pressure, a liter has a mass of 1.2506 grams. The gas condenses to a colorless liquid at 77.25 K and to a white solid at 63.3 K.
Nitrogen is chemically unreactive. It does not burn, and at ordinary temperatures it does not react with other elements. It is prepared commercially by distillation of liquid air. Liquid nitrogen is extremely useful in the laboratory for cooling and pumping applications.
Though mineral sources of nitrogen are rare, it does occur in a mercury sulfate called kleinite.
Nitrogen is an essential element in most of the substances which make up living organisms, including the proteins. Important compounds include fertilizers and explosives. An essential source of nitrogen for living organism is nitrogen fixation in plants since animal metabolisms cannot form the needed nitrogen compounds from N2 even though it is the major constituent of the atmosphere.
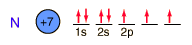
|