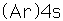Potassium
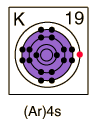 | Potassium, like the other alkali metals (Group I), is a sivery-white metal of very high chemical reactivity.
Potassium is one of the big 8 elements in the Earth's crust, being the seventh most abundant element at about 2.6% by weight. It is a constituent of many silicates including the orthoclase form of feldspar, one of the most abundant minerals on the earth. A silicate with aluminum, KAlSi3O8, forms the mineral microcline, which can be apple green to brown in color. A sulfate mineral of iron and potassium is jarosite.
|
Potassium chloride, KCl, forms colorless cubic crystals, resembling those of sodium chloride. Large deposits of potassium chloride are found at Stassfurt, Germany and near Carlsbad, New Mexico. It is also obtained from the Searles Lake in the Mojave Desert of California.
Potassium hydroxide, KOH, is a strongly alkaline substance.
Potassium hydrogen tartrate (KHC4H4O6), called cream of tartar, is a constituent of grape juice. It is used in making baking powder.
The principal use of potassium is as a fertilizer. Plant fluids contain large amounts of potassium ion which has been concentrated from the soil. Potassium sulfate and other salts of potassium are used to replace the soil potassium if it becomes depleted.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 26 |