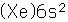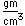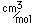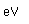Barium
Barium is a metal, but has no significant uses as such.
A significant medical use of barium is to enhance x-ray images of the intestinal tract. Barium has a high atomic number and absorbs x-rays strongly. A thin paste of barium sulfate, BaSO4, and water is is swallowed to coat the alimentary canal. This gives greater definition and contrast to the x-ray images of the tract. The low solubility of barium sulfate minimizes the toxic effects which might occur with other barium compounds. The mineral form of barium sulfate is called barite.
Barium nitrate Ba(NO3)2 and barium chlorate Ba(ClO3)2 are used for producing green fire from fireworks. Barium is used in the manufacture of paint pigments.
Barium appears in the carbonate mineral Benstonite. Barium carbonate, BaCO3, in mineral form is called Witherite.
Along with calcium, barium forms the carbonate mineral alstonite.
Barium appears in the phosphate mineral kulanite along with manganese.
An oxide formed along with manganese is called romanechite. Barium appears in an oxide of manganese with potassium called Hollandite. Barium appears with vanadium and lead in an oxide mineral of uranium, Francevillite
Barium is sometimes found in silicate minerals, for example hyalophane, (K,Ba)Al(Si,Al)3O8. The silicate Joaquinite contains barium along with iron, titanium and cerium. The silicates Brewsterite and heulandite contain barium along with strontium. Edingtonite is barium aluminum silicate of the zeolite group with the composition Ba[Al2Si3O10].4H2O.
|