Glutamine
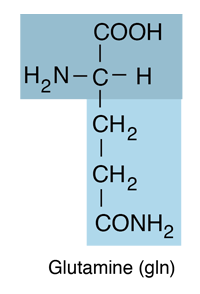 | Glutamine is an amino acid and belongs to the class which has neutral R-groups. It is polar and hydrophilic. In human blood, glutamine is the most abundant free amino acid. The dietary sources of glutamine includes especially the protein-rich foods like beef, chicken, fish, dairy products, eggs, vegetables like beans, beets, cabbage, spinach, carrots, parsley, vegetable juices and also in wheat, papaya, Brussels sprouts, celery, kale and fermented foods like miso. |
Glutamine contributes to the regulation of acid-base balance in the kidney by producing ammonium. It serves as a source of cellular energy next to glucose. It provides nitrogen donation for many anabolic processes, including the synthesis of purines. It is a source for carbon donation, refilling the TCA cycle. It serves as a nontoxic transporter of ammonia in the blood circulation.
Glutamine plays a role in maintaining the normal integrity of the intestinal mucosa.
Glutamine is one of the few amino acids that can directly cross the blood-brain barrier.
| Glutamine wiki |
Biochemical concepts
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Tillery, Enger and Ross
Ch 14
Ahern
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry *****Organic Chemistry | R Nave |