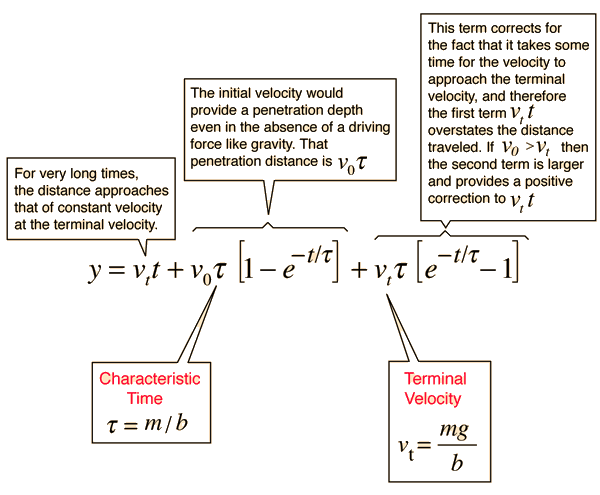
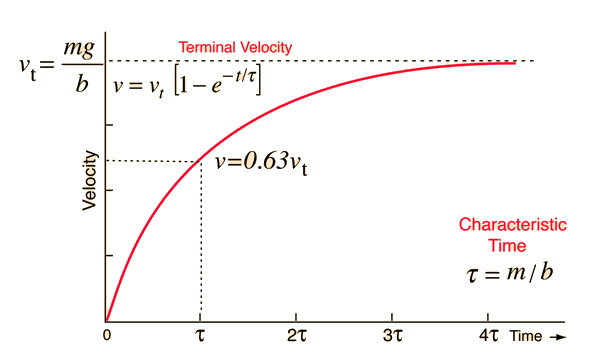
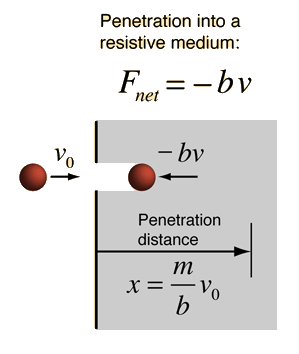
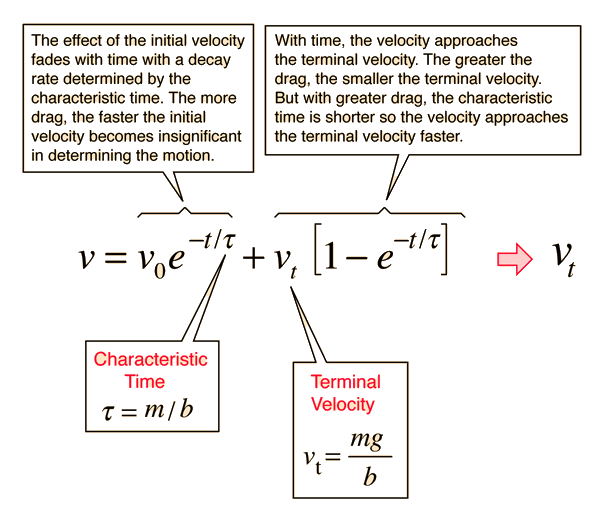
Velocity with Linear Drag
For an object that is acted upon by its weight, mg, and subject to a drag force proportional to its velocity -bv, the general form for the velocity is given by the expression below. For an object in a fluid, you must use an effective force mg' to account for the buoyancy of the fluid. For viscous drag, the drag coefficient b may be expressed in terms of the viscosity of the fluid. This velocity expression may then be integrated to obtain an expression for the distance.
| Motion equations | Graph of velocity | Distance details |
Fluid friction
| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics ***** Fluids | R Nave |