Steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes which alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi.
The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four "fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Steroids can also be more radically modified, such as by changes to the ring structure, for example, cutting one of the rings. Cutting Ring B produces secosteroids one of which is vitamin D3. | 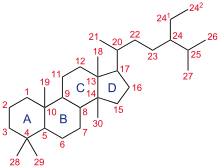 |
Examples include the lipid cholesterol, the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, and the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone.
| Steroid Wiki |
Biochemical concepts
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Matthews, van Holde and Ahern
Ch 10
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry | R Nave |