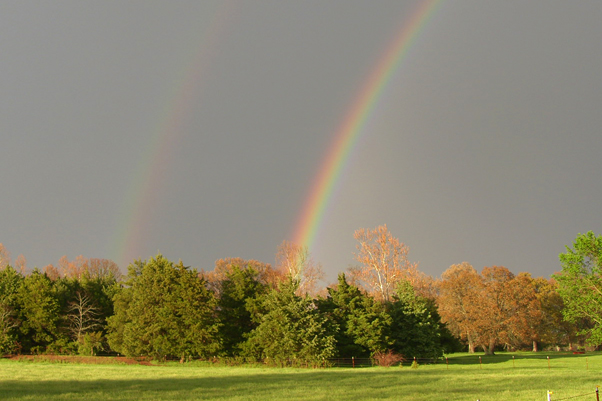
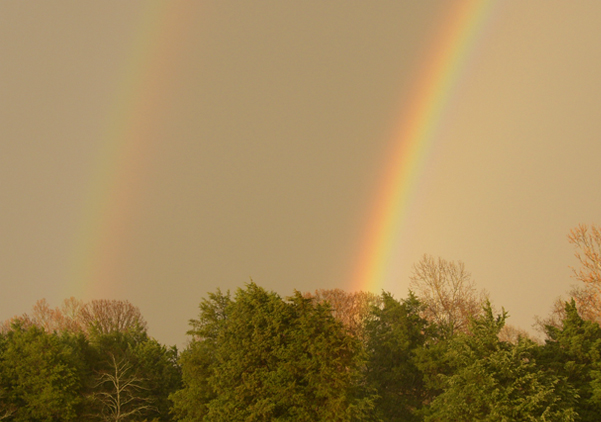
Rainbows
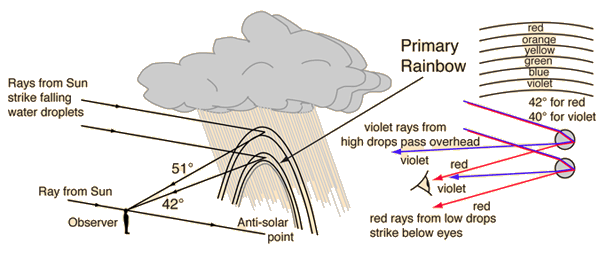
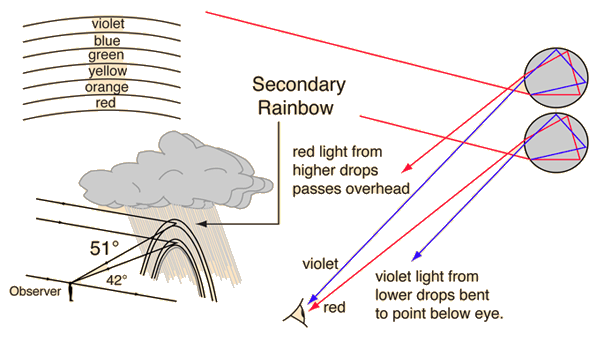
Rainbows result from refraction of sunlight in falling water droplets plus reflection of the light from the back of the droplet.
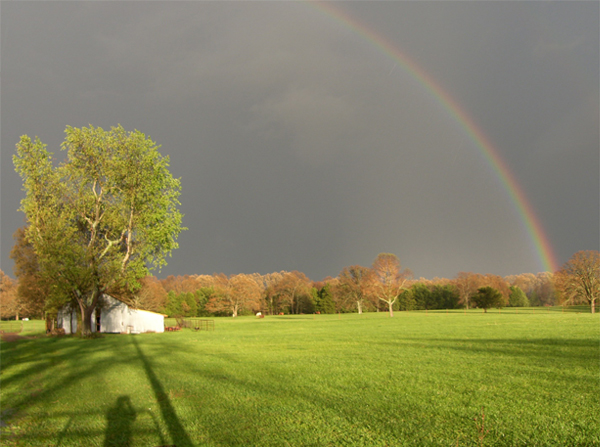
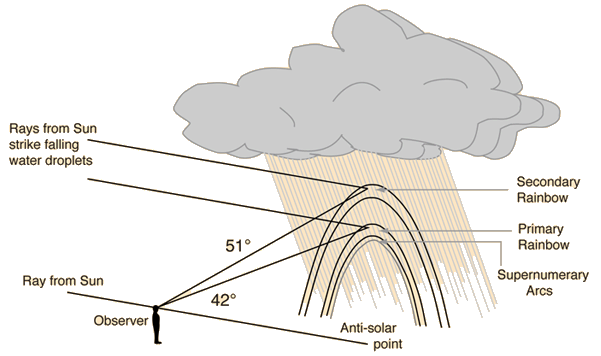

If during a rain shower you can see the shadow of your own head, then you are in position to see a rainbow if conditions are favorable. The rainbow forms a circular arc around the anti-solar point, which is located at the shadow of your head. You can search for the shadow of your head to find a rainbow in a waterfall, or even in the spray from a hose or sprinkler. (Photo by Dubby Waggoner, used by permission.)
|
 |
Rainbow concepts
Atmospheric optics concepts
References
Greenler
Schaaf
| HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision | R Nave |
 Photo by Dubby Waggoner, used by permission.
Photo by Dubby Waggoner, used by permission.