Organ of Corti
|
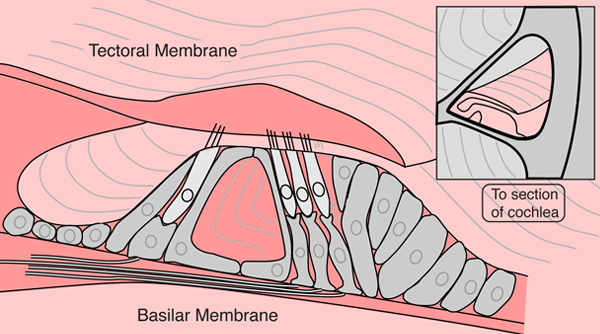
The organ of Corti is the sensitive
element in the inner ear and can be
thought of as the body's microphone. It is
situated on the basilar membrane in
one of the three compartments of the
Cochlea. It contains four rows of
hair cells which protrude from its
surface. Above them is the tectoral
membrane which can move in response
to pressure variations in the fluid-
filled tympanic and vestibular canals. There are some 16,000 -20,000 of the hair cells distributed along the basilar membrane which follows the spiral of the cochlea.
|
|
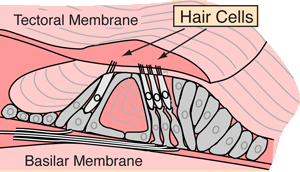
The place along the basilar membrane where maximum excitation of the hair cells occurs determines the perception of pitch according to the place theory. The perception of loudness is also connected with this organ.
Tiny relative movements of the layers of the membrane are sufficient to trigger the hair cells. Like other nerve cells, their response to stimulus is to send a tiny voltage pulse called an "action potential" down the associated nerve fiber (axon). These impulses travel to the auditory areas of the brain for processing.
|