Apollo Moon Exploration
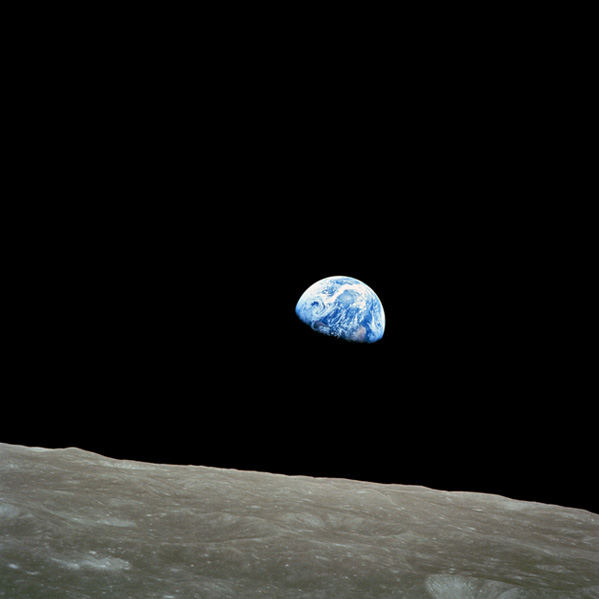
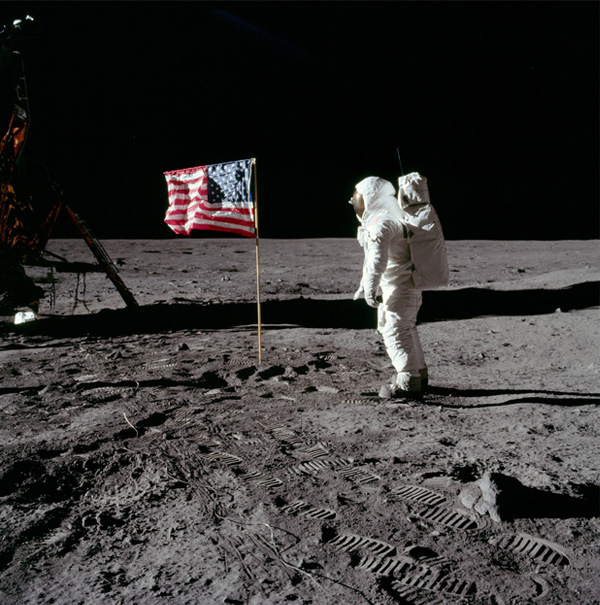
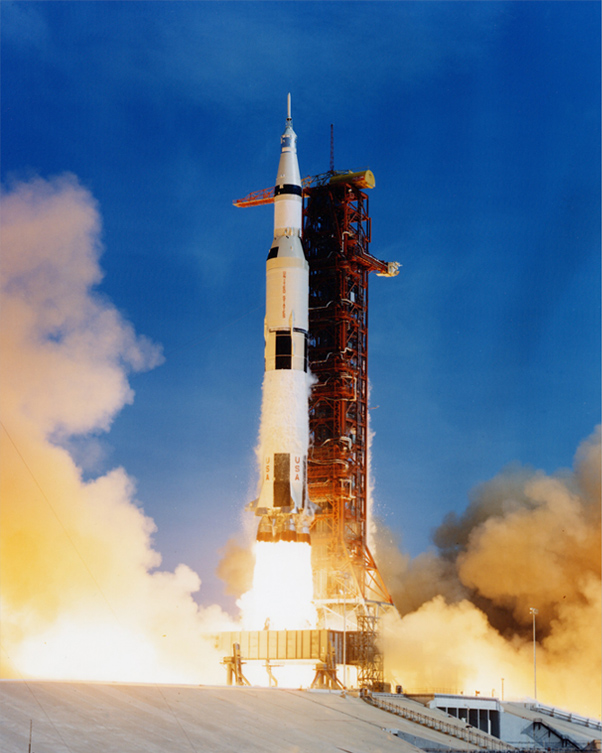
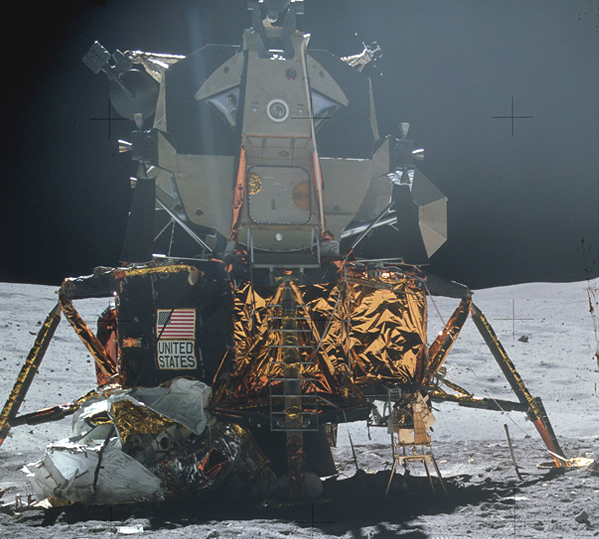
 | The Apollo Moon exploration missions were the culmination of a long series of missions beginning in 1964 which included the U.S. Ranger, Surveyor, and Orbiter programs and the U.S.S.R. Luna and Zond programs. There were also six one-man Earth orbiting missions (Mercury) and ten two-man orbital flights (Gemini) in the early sixties in preparation for lunar missions. The Apollo 7 mission orbited the Earth in final preparation for the Moon vogages and the Apollo 8-10 missions orbited the Moon but did not land. In the period 1969 to 1972, Apollo 11, 12 and Apollo14 - 17 landed on the moon. Apollo 13 experienced an explosion enroute and was looped around the Moon and back to the Earth barely in time to save the crew. |
Apollo 11 and 12 landed in smooth lunar maria, while Apollo 14-17 reached more rocky and mountainous regions to widen the variety of samples collected.
| Apollo 7-10 | Apollo 11 | Apollo 12 | Apollo 13 |
| Apollo 14 | Apollo 15 | Apollo 16 | Apollo 17 |
| Apollo Spacecraft | Landing sites |
Online references:
NASA's Apollo Program site
Wiki: Apollo Program
NASA History: The Apollo Program
Apollo landing sites
Solar System Illustration
Solar System Concepts
Moon Concepts
| HyperPhysics********** Astrophysics | R Nave |