The Nervous System
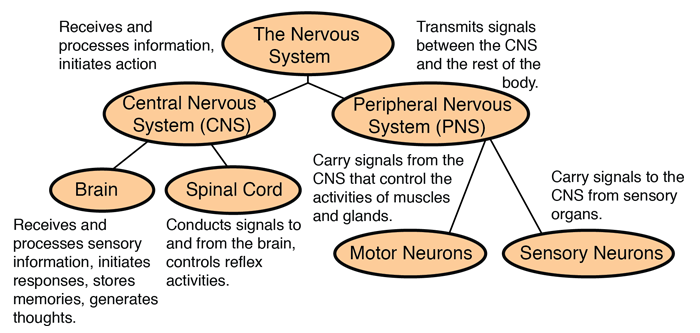
The nervous system is a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It can be considered to be made up of two parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is made up of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. The peripheral nervous system of sensory neurons and clusters of such neurons (ganglia) and nerves that connect to one another and to the central nervous system. The following outline follows the content of Audesirk & Audesirk.
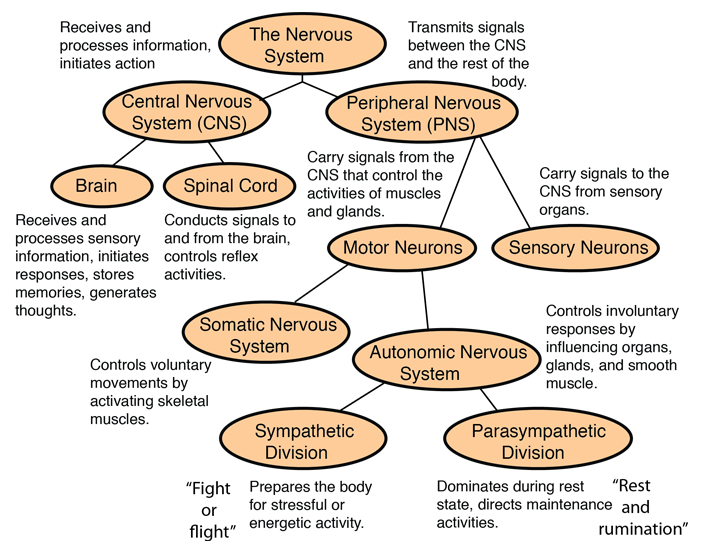
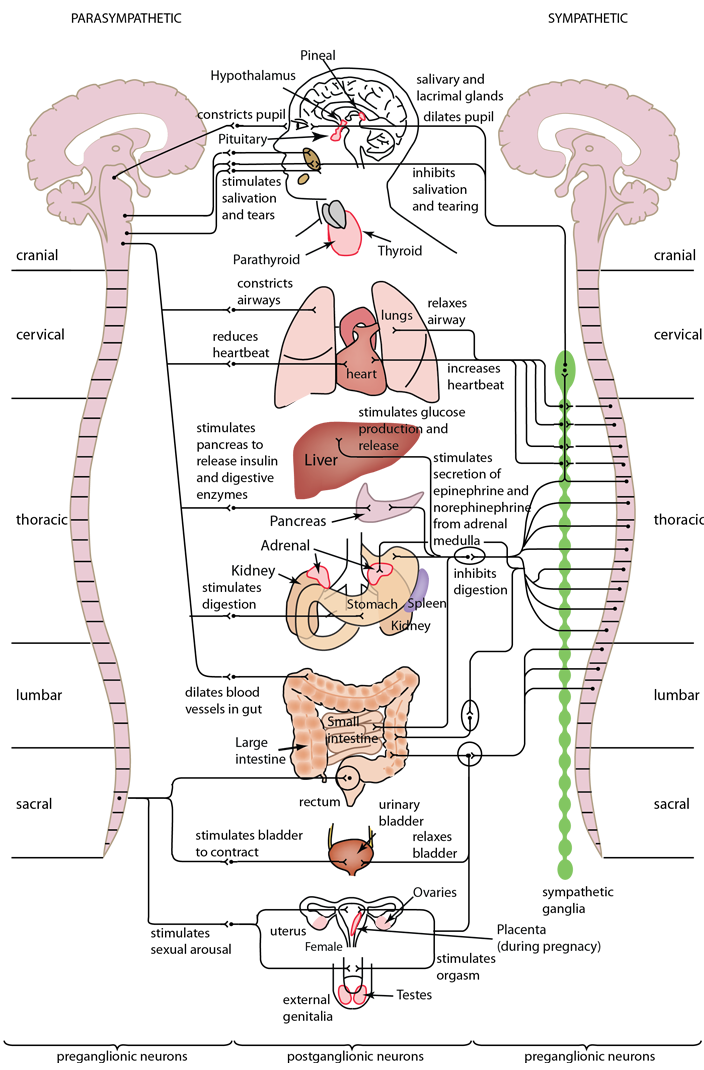
The nervous system has two main subdivision: the somatic, or voluntary, component, and the autonomic, or involuntary, component. The autonomic nervous system regulates many body process such as blood pressure and rate of breathing, that work without conscious effort. The somatic system consists of nerves that connect the brain and spinal cord with muscles and sensory receptors in the skin.
The primary function of the autonomic nervous system is homeostasis. It has two divisions: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system accelerates heart rate, constricts blood vessels, and raises blood pressure, and other functions of a generally stimulating nature. The parasympathetic nervous system slows heart rate, increases intestinal and gland activity, and other inhibitory or calming functions.
| This material is part of a brief overview of the topics studied in biology with the intent to highlight the connections to basic ideas in physics and physical science. |
Reference
Audesirk & Audesirk
Ch 33
Livescience
| HyperPhysics***** Biology | R Nave |