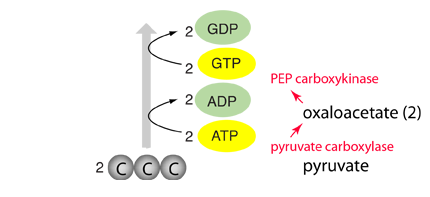
Gluconeogenesis
The synthesis of molecules on the chain from pyruvate to glucose is called gluconeogenesis. It is largely the reverse of the successive chain of events of glycolysis, but there are some differences which will be noted here.
Glucose is made from pyruvate in gluconeogenesis at the cost of 4 ATP, 2 GTP, and 2 NADH. The breakdown pathway of glucose in glycolysis yields 2 ATP and 2 NADH. So it takes 4 more energetic triphosphates of energy to make each molecule of glucose than can be obtained from glucose breakdown. But keeping the supply of glucose nearly constant is so essential that many routes to pyruvate are used to feed into the process. The most common feeder molecules are alanine and lactate, which can be converted to pyruvate in a single step.
The final step to glucose is made with the use of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase, which clips off a phosphate group. | 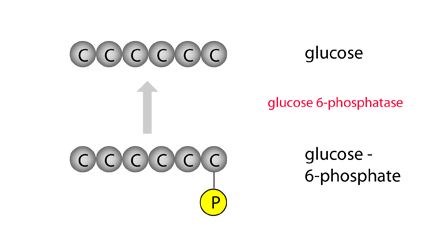 |
A rearrangement of the molecule forms glucose-6-phosphate. | 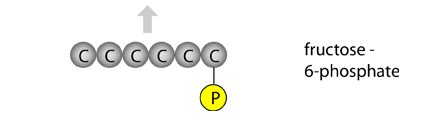 |
Departing from the reverse of glycolysis, a different enzyme, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, is used to snip off a phosphate. | 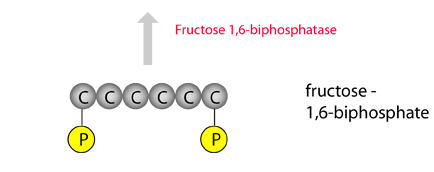 |
Following the reverse of the glycolysis steps, we reach fructose-1,6-biphosphate. | 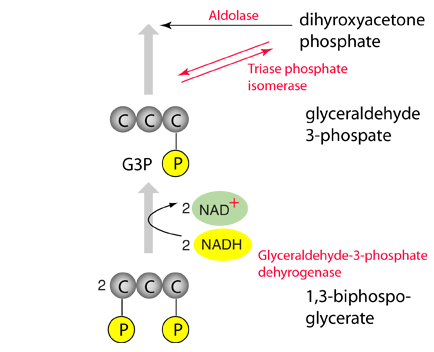 |
Two molecules of high energy ATP are used to accomplish the reversal of the glycolysis reactions to produce 2 molecules of 1,3-biphosphoglycerate. | 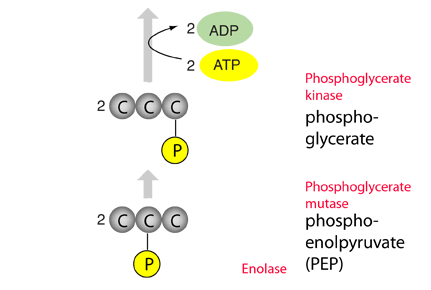 |
| Cellular Respiration |
Reference
Enger & Ross
Ch 6
Audesirk & Audesirk
Ch 8
Ahern , Ch 15.
| HyperPhysics***** Biology | R Nave |