Radiometric Dating and the Passage of Time
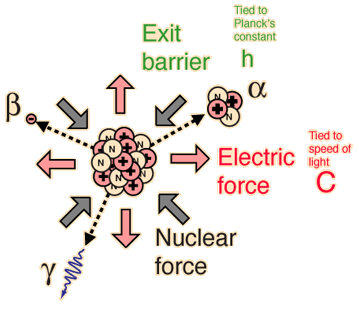
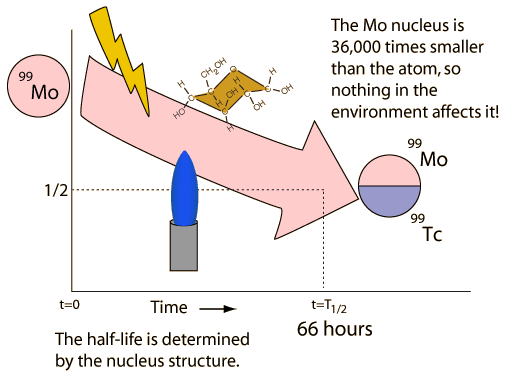
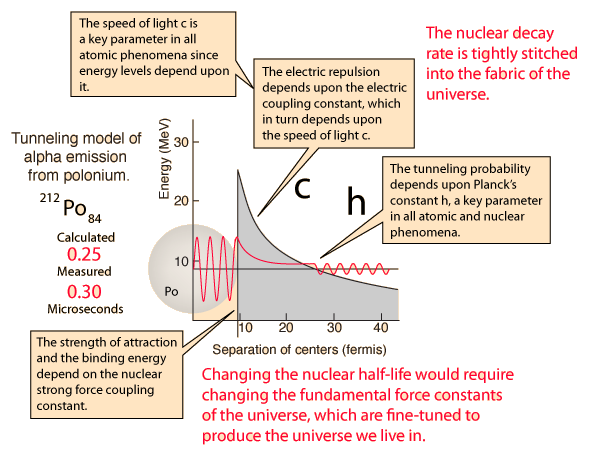
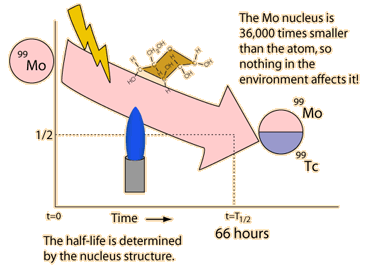 | Nuclear decay is a reliable clock because essentially nothing in nature affects it. |
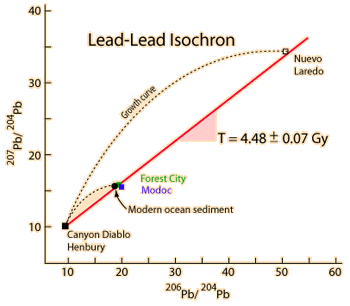
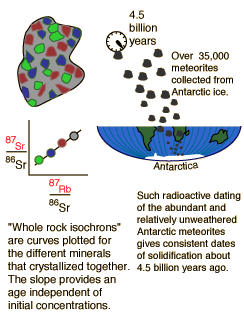
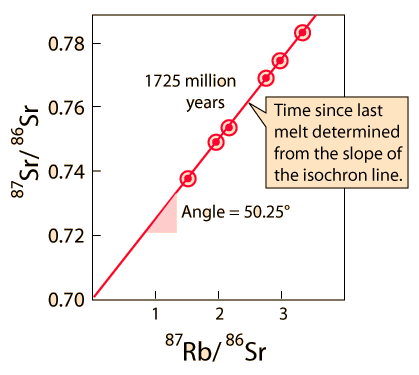
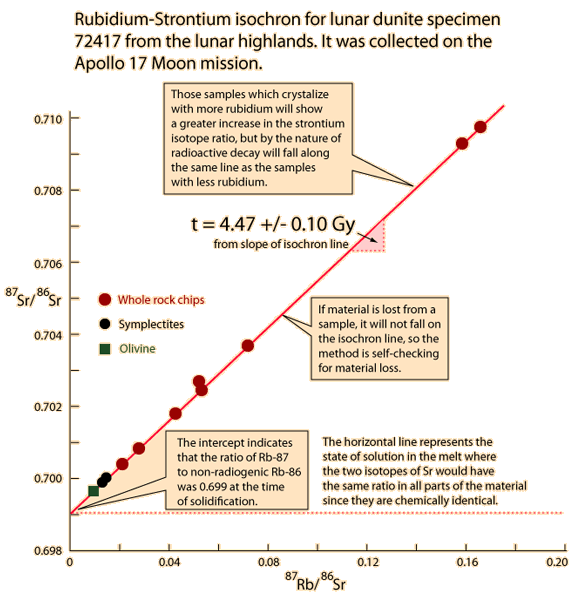
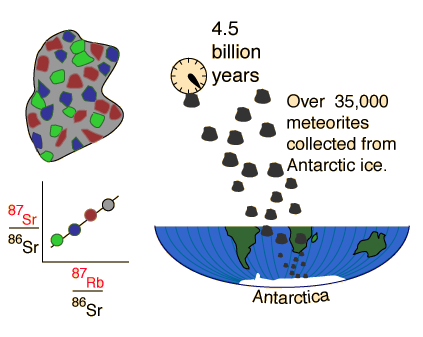
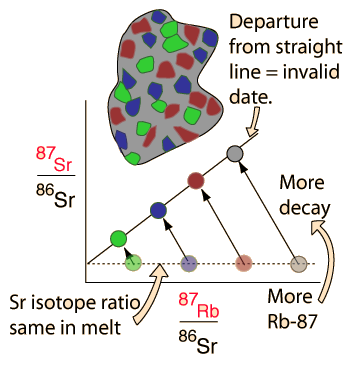 | Whole-rock isochron methods measure the time to the last melting of the rock and allow evaluations of initial concentrations. Melting resets the clock since all isotopes are chemically identical. Non-radiogenic isotopes (like strontium-86) provide a reference for the process. |
The same whole-rock tests on moon rocks give similar ages. | 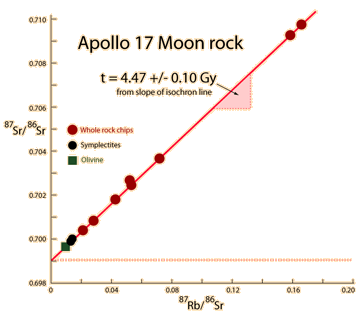 |
| Outline |
| A brief overview of time |
| Book of Nature | R Nave |